
Repair – In certain instances, the ACL torn ends may be sutured together.Reconstruction - The torn ACL is removed and is reconstructed using tendons from the patient’s own knee or using an “allograft” or cadaver tendon.Depending on the technique used to reconstruct the ligament, the number and size of the incisions may vary.The surgery is performed arthroscopically.Tears may enlarge over time if not treated. Smaller tears have better outcomes than larger tears.If you continue to have knee pain, instability, locking or other symptoms despite therapy and medications.
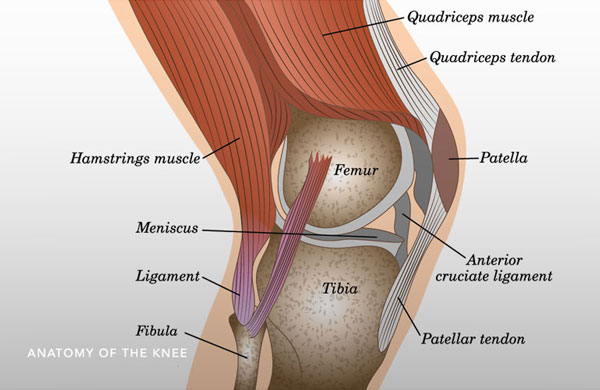
#Where is your acl located full
Return to full recovery is multi-factorial and depends on the procedures performed, patient age, as well as the surgical technique. The recurrence rate for ACL tears after surgery is variable (less than 10%). The success rate for ACL reconstruction depends on several factors including: the chronicity of the ACL tear, the status of the cartilage in the rest of the knee, the type of graft utilized, the type of graft fixation, whether there is knee mechanical mal-alignment of the femur and tibia bones, and the level of activity the patient wishes to return to after surgery. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery can be performed as an outpatient procedure with an arthroscope, or minimally invasive camera procedure. Your orthopedic surgeon can best advise you as to the appropriate treatment strategy.

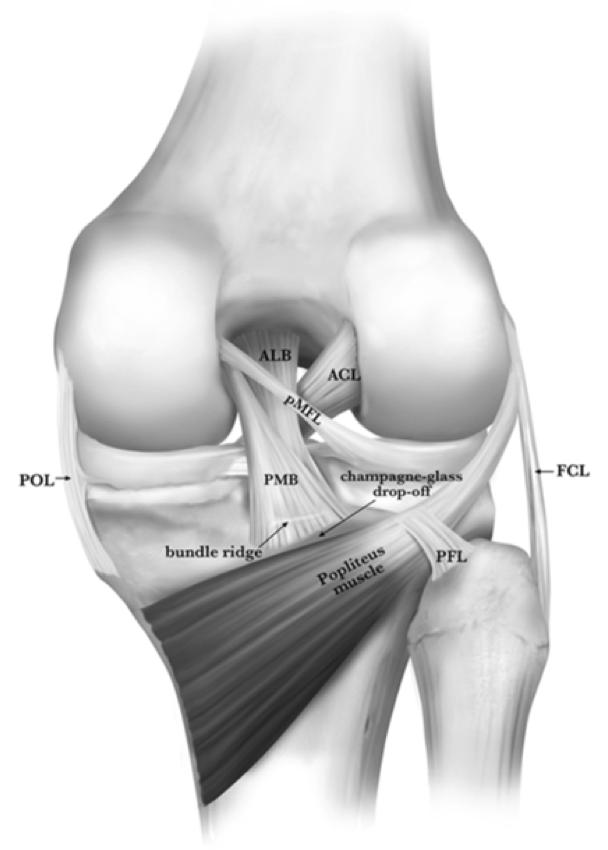
Patients with meniscus tears may require meniscus repair or meniscectomy. A torn ligament generally cannot be repaired and must be reconstructed. Patients with associated meniscus tears or significant cartilage tears may also be advised to proceed with surgery to prevent further injury to cartilage and to repair cartilage tears.
#Where is your acl located professional
Certain patients, such as professional and recreational athletes, dancers, and those whose physical activities require pivoting are ideal candidates for surgery. Therapy, bracing, and activity modification may be recommended to the first and second type of patients, whereas surgery may be recommended for the third. The third type of patient has significant instability and is unable to function with the ACL tear. The second type of patient has instability episodes, however the patient is able to cope, with only limited symptoms. The first category is the patient who does not demonstrate significant instability. Patients with complete ACL tears may be sub-divided into three general categories based on knee symptoms. Your doctor may recommend an aspiration to remove accumulated knee fluid to allow for faster return to full range of motion. Initial treatment may require ice, compression and elevation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
